| CAS NO: | 1001600-56-1 |
| 规格: | ≥98% |
| 包装 | 价格(元) |
| 2mg | 电议 |
| 5mg | 电议 |
| 10mg | 电议 |
| 25mg | 电议 |
| 50mg | 电议 |
| 100mg | 电议 |
| 250mg | 电议 |
| Molecular Weight (MW) | 1205.57 |
|---|---|
| Formula | C70H96N10O8.xCF3COOH |
| CAS No. | 1001600-56-1(free base) |
| Storage | -20℃ for 3 years in powder form |
| -80℃ for 2 years in solvent | |
| Solubility (In vitro) | DMSO: 100 mg/mL (82.9 mM) |
| Water: 25 mg/mL (20.73 mM) | |
| Ethanol: 100 mg/mL (82.9 mM) | |
| Other info | Synonym: BV6; BV-6; BV 6; Smac mimetic BV6; InChi Key: DPXJXGNXKOVBJV-YLOPQIBLSA-N InChi Code: InChI=1S/C70H96N10O8/c1-47(71-3)63(81)75-59(53-37-21-11-22-38-53)69(87)79-45-27-41-55(79)65(83)77-61(57(49-29-13-7-14-30-49)50-31-15-8-16-32-50)67(85)73-43-25-5-6-26-44-74-68(86)62(58(51-33-17-9-18-34-51)52-35-19-10-20-36-52)78-66(84)56-42-28-46-80(56)70(88)60(54-39-23-12-24-40-54)76-64(82)48(2)72-4/h7-10,13-20,29-36,47-48,53-62,71-72H,5-6,11-12,21-28,37-46H2,1-4H3,(H,73,85)(H,74,86)(H,75,81)(H,76,82)(H,77,83)(H,78,84)/t47-,48-,55-,56-,59-,60-,61-,62-/m0/s1 SMILES Code: O=C([C@H]1N(C([C@H](C2CCCCC2)NC([C@@H](NC)C)=O)=O)CCC1)N[C@@H](C(C3=CC=CC=C3)C4=CC=CC=C4)C(NCCCCCCNC([C@@H](NC([C@H]5N(C([C@H](C6CCCCC6)NC([C@@H](NC)C)=O)=O)CCC5)=O)C(C7=CC=CC=C7)C8=CC=CC=C8)=O)=O |
| Chemical Name | N,N'-(hexane-1,6-diyl)bis(1-{(2S)-2-cyclohexyl-2-[(N-methyl-L-alanyl)amino]acetyl}-L-prolyl-beta-phenyl-L-phenylalaninamide):trifluoroacetic acid(1:x) |
| In Vitro | BV6 inhibits the cell viability of HCC193 NSCLC cells with IC50 of 7.2 μM, induces apoptosis in both HCC193 and H460 cell lines, and also significantly enhances the radiosensitivity of these cell lines through activation of cleaved caspase-8 and cleaved caspase-9, respectively. In immature dendritic cells, BV-6 treatment results in moderate activation of the classical NF-kB pathway. Furthermore, BV-6 increases CIK cell-mediated lysis of hematological (H9, THP-1, and Tanoue) and solid malignancies (RH1, RH30, and TE671). BV-6 also enhances apoptosis of peripheral blood mononuclear cells and most notably has an inhibitory effect on immune cells limiting their cytotoxic potential |
|---|---|
| In Vivo | Murine cIAP-1, cIAP-2 and XIAP expressions are clearly observed in the cytoplasm of both epithelial and stromal cells of implants, whereas Survivin is mainly expressed in the nuclei BV6 treatment for 4 weeks attenuated the intensity of IAPs expression. The size of lesions range from ~2 to 7 mm in diameter. The monolayer epithelial cell lining of the cyst is shown. After immunohistochemical staining, cytokeratin and vimentin are positively stained, whereas calretinin is negative. After BV6 treatment for 4 weeks, the total number of lesions (4.6 versus 2.8/mouse), the average weight (78.1 versus 32.0 mg/mouse) and the surface area (44.5 versus 24.6 mm2/mouse) of lesions are significantly less than in the controls. In the endometrial gland epithelia or stroma, the percentage of Ki67-positive cells decreases after BV6 treatment. |
| Animal model | Mice: Female mice (6 weeks of age, BALB/c) are used. All 24 mice are ovariectomized through a 1 cm longitudinal skin incision then injected s.c. with estradiol valerate (0.5 μg/mouse/week) once per week for 6 weeks until the experimental endometriosis induction. Two weeks after ovariectomy, the uteri of an additional eight donor mice (n=8) are removed en bloc after euthanasia and cleaned of excess tissue in sterile saline. Each uterus is cut to include the uterine horns in each half with a linear incision longitudinally and minced (0.5 mm in diameter) with dissecting scissors. The ovariectomized recipient mice (n=16) are anesthetized using pentobarbital sodium. A 0.5 cm subabdominal midline incision is made. Each recipient receives half of the donor uterus (1:2 donor uterus to host ratio) minced and added to 500 μl saline, and injected into the peritoneal cavity, and the peritoneum is sutured. Injected uterine tissue weighed ~50 mg per mouse. For the next 4 weeks, recipient mice are treated with a single i.p. injection of BV6 (n=8; 10 mg/kg) or vehicle (n=8; 1% DMSO) twice weekly. |
| Formulation & Dosage | 10 mg/kg; i.p. |
| References | Li W, et al. J Thorac Oncol. 2011, 6(11), 1801-1809.; Uegaki T, et al. Inhibitor of apoptosis proteins (IAPs) may be effective therapeutic targets for treating endometriosis. Hum Reprod. 2015 Jan;30(1):149-58. |
 SMAC mimetic BV6 induces cell death in monocytes. SMAC mimetic BV6 induces cell death in monocytes.
| 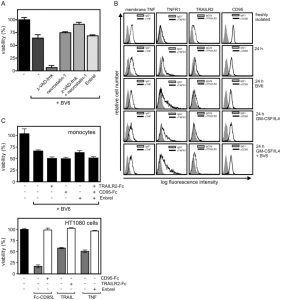 Müller-Sienerth N, et al. PLoS One. 2011, 6(6), e21556 |
